Evaluating Dynamic Loads
Evaluating Dynamic Loads in Piping Systems Caused by Waterhammer
 |
|
High transient forces fail reducer connection |
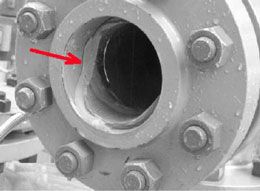 |
| Unsupported pipe fails from transient pressure plus the bending caused by initial failure at reducer |
In some cases, hand calculations and conservative assumptions can be used to predict the magnitude, direction, location and timing of these dynamic loads. In many cases however, the complexity of waterhammer loading renders manual methods useless, requiring computer analysis to properly predict the loading seen by a piping system.
Once these loads are determined, pipe stress software can be used to evaluate the piping system response, such as deflections, restraint loads, equipment loads and stresses.
This paper examines a waterhammer event caused by the partial closing of a valve in a relatively simple system. The hydraulic transient analysis is performed using AFT Impulse, and the mechanical system response is then evaluated using Intergraph’s CAESAR II ® pipe stress analysis software.
One direct benefit of using these two particular applications is that AFT Impulse creates force-time data files for direct import into CAESAR II.
A zip file of the files used to prepare this paper can be downloaded here: English Units; Metric Units


