Gas accumulators can have a bladder separator, as well as a differential orifice plate. Both can be modeled in AFT Impulse.
Resources
Product Tip – Making a Difference, No Power Needed
Product Tip – Using Liquid Accumulators in AFT Impulse
]]>
AFT Fathom and the AFT Fathom Settling Slurry Add-on Module
AFT Impulse and the AFT Impulse Settling Slurry Add-on Module
- Covers the minimum requirements for reciprocating positive displacement pumps for use in service in the petroleum, chemical, and gas industries. Both direct-acting and power-frame types are included.
- Defines topics such as maximum and minimum speeds, pulsation and vibration control requirements, and testing requirements.
- API RP520: Design and Installation of Pressure Relieving Systems in Refineries (recommended practice)
- ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Sec. VIII-Non-Mandatory Appendix M
- ISO 4126-9 Safety Devices for Protection Against Excessive Pressure -Mandatory.
- All three standards have different requirements for the inlet piping to the relief valve and the discharge piping. They also can vary depending on the operating conditions, the gas involved, and the type of relief valve used.
- Contains requirements for piping typically found in petroleum refineries; chemical, pharmaceutical, textile, paper, semiconductor, and cryogenic plants; and related processing plants and terminals. It covers materials and components, design, fabrication, assembly, erection, examination, inspection, and testing of piping.
- This Code applies to piping for all fluids including:
(1) raw, intermediate, and finished chemicals;
(2) petroleum products;
(3) gas, steam, air and water;
(4) fluidized solids;
(5) refrigerants; and
(6) cryogenic fluids.
]]>
- Prescribes requirements for the design, materials, construction, assembly, inspection, testing, operation, and maintenance of liquid pipeline systems between production fields or facilities, tank farms, above- or belowground storage facilities, natural gas processing plants, refineries, pump stations, ammonia plants, terminals (marine, rail, and truck), and other delivery and receiving points, as well as pipelines transporting liquids within pump stations, tank farms, and terminals associated with liquid pipeline systems.
- Also prescribes requirements for the design, materials, construction, assembly, inspection, testing, operation, and maintenance of piping transporting aqueous slurries of nonhazardous materials such as coal, mineral ores, concentrates, and other solid materials, between a slurry processing plant or terminal and a receiving plant or terminal.
]]>
]]>
]]>
Resources
Product tip – What About Viscosity Corrections?
]]>AFT Impulse offers two transient cavitation models: The Discrete Vapor Cavity Model and the Discrete Gas Cavity Model.
]]>AFT software allows users to model centrifugal pumps, fans, and compressors by inputting the respective curve. Based on the system hydraulics, the location of the curve on which the pump, fan, or compressor will operate is determined.
These calculations allow engineers to assess the suitability of a centrifugal pump, fan, or compressor by reporting a wide range of parameters including head rise, flow rate, NPSHA (for pumps), and speed, as well as efficiency, BEP, and NPSHR (for pumps) with additional input.
- AFT Arrow used centrifugal fans and compressors
- AFT Fathom & AFT Impulse use centrifugal pumps
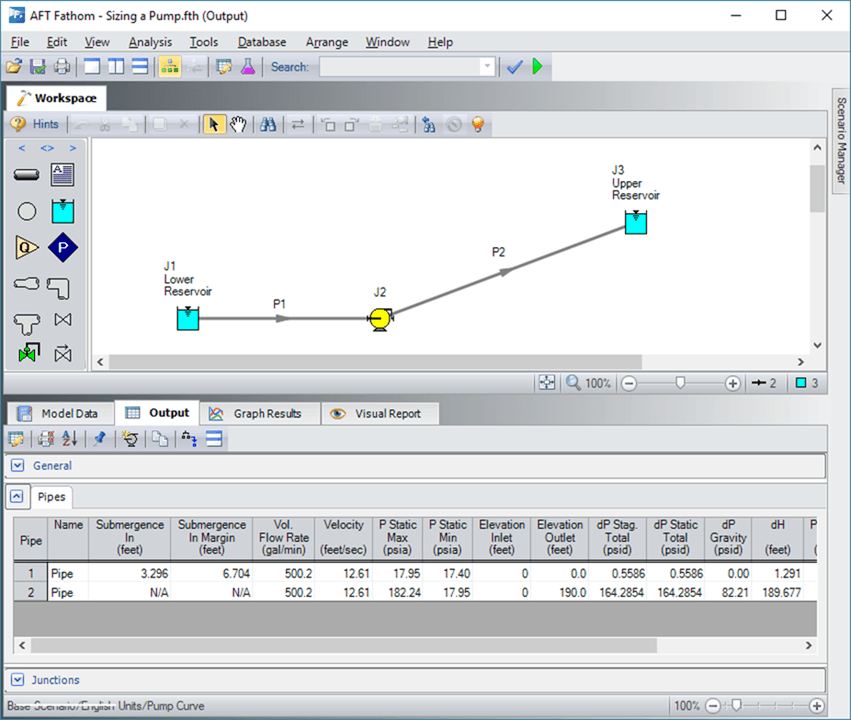
In AFT Fathom, The Pump Properties window provides clear distinction between rotodynamic (or centrifugal) and positive displacement pumps. Note that PD pump models can calculate acceleration head in the suction line and AFT can also model multistage pumps with interstage takeoff flows.
The Hydraulic Institute wrote an article highlighting centrifugal pumps: https://www.pumpsandsystems.com/how-centrifugal-pumps-work
]]>
|
AFT Fathom
|
AFT Arrow
|
AFT Impulse
|
]]>
Resources
Product tip – Feeling Compressed? Don’t Forget Your Thermodynamics
]]>Using various pipe friction models, AFT Arrow allows users to be compliant with NFPA regulations regarding dust collection systems. Strong correlation to field data has been found to exist using this feature in a published case study (see Case Study 1).
Resources
Case study 1 – AFT Arrow Results Support Manufacturing Facility Data – Dust Collection Systems Rebalanced
]]>Resources
Product Tip – Using Equivalent Lengths in AFT Fathom
]]>